I upgraded to GitHub Copilot Pro+ plan to test its capabilities for unit test generation, code smell detection, code translation, refactoring and much more.
If you are curious to know “Is GitHub Copilot Worth It?” then this Copilot review is for you.
To find out whether GitHub Copilot is worth it or not, I thoroughly analyzed its core features for accuracy and reliability.
Let’s get started with this in-depth GitHub Copilot review.
At a Glance
| GitHub Copilot features | Editor’s views |
| Supported Programming Languages | Excellent. Almost all programming languages are supported. |
| Code Completion | Good. Can be improved if it could understand entire codebase. |
| Detect Code Smells | No. You must look for some alternative like Bito. |
| Write Unit Tests | Absolutely yes! It’s great. |
| Refactor Code | Good. Can really speed up development. |
| Code Translation | Less reliable. Sometimes it does not even work. |
| Software Documentation | Good. But it requires manual work. |
| Code Review | Copilot’s reviews are surface-level and nitpicky. I recommend trying Bito’s AI Code Review Agent for deeper, more reliable insights. |
Just in case you have never heard about GitHub Copilot before, let me briefly describe it for you.
What is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot is an Artificial Intelligence based coding assistant that helps you write code faster by suggesting entire lines or blocks of code. It leverages advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4.5 and integrates with various development environments.
Now you might be wondering how GitHub Copilot knows what to suggest?
Basically, GitHub Copilot knows what to suggest by analyzing the context of your code—including the file you’re working in, surrounding lines of code, comments, function names, and even the structure of your project. The powerful AI models it uses are trained on billions of lines of public code from GitHub and other sources. This allows it to recognize patterns and generate relevant, context-aware code suggestions in real time.
Updated Features and Enhancements (2025)
- Agent Mode: Copilot now includes an Agent Mode that enables it to iterate on its own output, recognize and fix errors automatically, suggest terminal commands, and analyze run-time errors with self-healing capabilities.
- Next Edit Suggestions: This feature accelerates code changes by automatically identifying and proposing the next edit based on the context of previous changes.
- Copilot Extensions: Developers can now integrate and prompt their favorite tools directly in Copilot Chat using natural language, enhancing workflow efficiency.
- Vision Input: Copilot now supports image-based input processing, allowing developers to provide screenshots with annotations or markup to guide the AI in generating actionable code.
- Code Review: Copilot offers a code review feature that helps offload basic reviews to a Copilot agent, identifying bugs, potential performance problems, and suggesting automatic fixes.
- Copilot Pro+: A new individual tier for developers, Copilot Pro+ offers exclusive access to the latest models (GPT-4.5), priority access to previews, and 1500 premium requests per month.
GitHub Copilot Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Speeds up coding with real-time suggestions.
- Supports multiple programming languages.
- Integrates with VS Code, JetBrains, and Neovim.
- Offers access to advanced models (GPT-4.5, Claude, etc.) in paid plans.
- Includes chat-based assistance for debugging and documentation.
Cons:
- May suggest insecure or incorrect code.
- Lacks full context of large codebases.
- High-end plans can be expensive for individual users.
- Doesn’t replace human code reviews.
Supported Programming Languages and IDEs
GitHub Copilot supports all programming languages, libraries, and frameworks that are used in public GitHub repositories.
The reason is simple. GitHub Copilot has been trained using an extensive dataset of publicly available source code, which includes code extracted from GitHub repositories, spanning billions of lines.
Currently, GitHub Copilot may not be able to assist you with the recently released libraries and APIs. However, as more examples are made available and integrated into its training set, the relevance of its suggestions improves over time. They even have plans to include methods for emphasizing the significance of newer APIs and samples in GitHub Copilot’s suggestions.
GitHub Copilot can be integrated with:
Setting up GitHub Copilot
To start using Copilot, you need a GitHub account and an active GitHub Copilot subscription.
GitHub Copilot offers several subscription plans tailored to individual developers, educators, and organizations. Here’s a concise overview of each plan:
GitHub Copilot Free
- Eligibility: Available to individual developers not managed by an organization or enterprise.
- Features:
- Up to 2,000 code completions per month.
- 50 agent mode or chat requests per month.
- Access to models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4.1.
- Cost: Free.
GitHub Copilot Pro
- Designed for: Individual developers seeking enhanced capabilities.
- Features:
- Unlimited code completions.
- Unlimited agent mode and chats with GPT-4.1.
- Access to code review, Claude 3.7/4.0 Sonnet, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and more.
- Six times more premium requests than the Free plan, with the option to purchase additional requests.
- Pricing:
- $10 USD per month
- $100 USD per year
- Trial: 30-day free trial available.
- Free Access: Available to verified students, teachers, and maintainers of popular open-source projects.
GitHub Copilot Pro+
- Designed for: Individuals requiring maximum flexibility and model choice.
- Features:
- All Pro features included.
- Access to all models, including Claude 4.0 Opus, o3, and GPT-4.5.
- Thirty times more premium requests than the Free plan, with the option to purchase additional requests.
- Access to the Coding Agent (preview).
- Pricing:
- $39 USD per month
- $390 USD per year
- Note: No trial period; billing starts immediately upon subscription.
GitHub Copilot Business
- Designed for: Organizations and teams.
- Features:
- All Pro features included.
- Centralized management and Copilot policy control for organization members.
- 300 premium requests per user per month.
- Pricing: $19 USD per user per month.
GitHub Copilot Enterprise
- Designed for: Large enterprises requiring advanced features.
- Features:
- All Business features included.
- Access to the Coding Agent.
- Additional enterprise-grade capabilities.
- 1,000 premium requests per user per month.
- Pricing: $39 USD per user per month.
In the examples given below, I will be using “GitHub Copilot Pro+” plan.
To install Copilot in Visual Studio Code (VSCode), you can easily find the Copilot extension in the VSCode marketplace. Simply search for “GitHub Copilot”, select the extension, and click on the install button to add it to your IDE.
GitHub Copilot Shortcuts
Please remember these shortcuts. We will use them later in our examples below.
| Description | Press on Keyboard |
| Accept suggestion | Tab |
| Dismiss suggestion | Esc |
| Show next suggestion | macOS: Option (⌥) + ] Windows/Linux: Alt + ] |
| Show previous suggestion | macOS: Option (⌥) + [ Windows/Linux: Alt + [ |
| Trigger inline suggestion | macOS: Option (⌥) + \ Windows/Linux: Alt + \ |
| Open suggestions in separate pane | macOS: Option (⌥) + Return Windows/Linux: Alt + Enter |
Is Copilot Good at Code Completions?
GitHub Copilot generally provides high-quality code completions. However, if the suggested completions are not as accurate in your specific case, you may need to write additional code or provide explicit instructions to help GitHub Copilot better understand the context and generate more precise solutions.
Let me show you an example of code completion suggested by GitHub Copilot. Check its quality and completeness, you will love it.
I started by creating a new Python file called “main.py”
If you have an empty file, Copilot will not provide any suggestions. It requires initial instructions or source code to understand the context and generate relevant suggestions.
So, I wrote the below instructions in Python comment and pressed the “Enter” key.
# Write a function that take a string title and convert it to a URL slug. Don't use external libraries. Make sure to trim leading and trailing spaces, replace spaces with dashes, lowercase the slug, remove special characters, and finally remove consecutive dashes from slug.
# (e.g. " This Is My Title! " to "this-is-my-title")
That’s where the magic of Copilot starts.
GitHub Copilot began suggesting lines of code (one by one), sometimes even entire code snippets. To complete the program, I had to accept each suggested line by pressing the “Tab” key.
However, there are times when the suggested code does not meet your specific needs. In such cases, you can either try alternative suggestions using the shortcut keys I mentioned above or simply write some more code manually to help Copilot understand your requirements and provide better suggestions.
Screenshot of GitHub Copilot Code Suggestions:
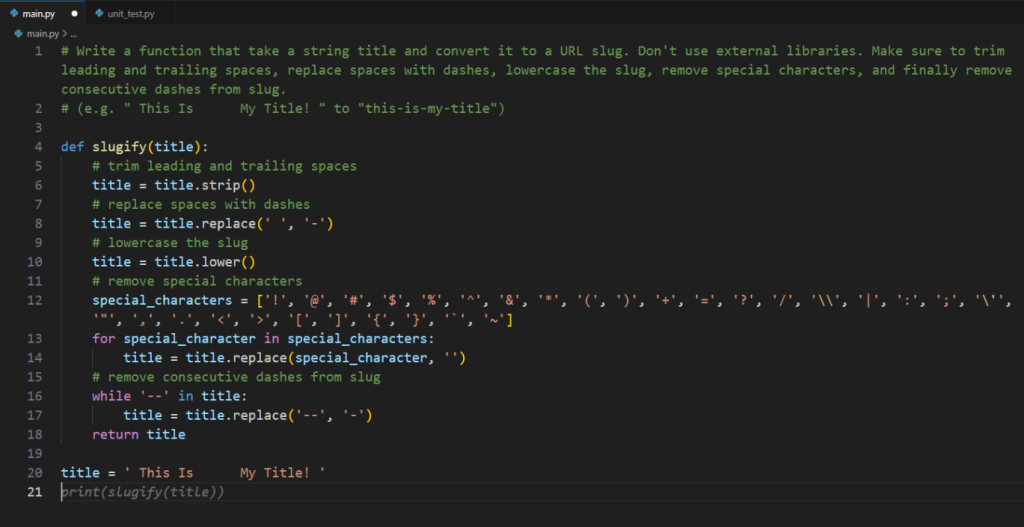
You can see that the suggested code meets all the requirements I mentioned. Now, when we run this code, it will convert any string to a URL-friendly slug correctly.
Output:

Can GitHub Copilot Detect Code Smells?
No. GitHub Copilot finds it difficult to detect and fix code smells. While it has some knowledge of basic code smells like Duplicate Code and Long Parameter List, it usually struggles with more complex ones like Shotgun Surgery, Data Clumps, Parallel Inheritance Hierarchies, and others.
In this review, I will provide an example of Shotgun Surgery and demonstrate how Copilot fails to solve it.
Shotgun Surgery Code Smell (The Challenge):
Suppose you have an e-commerce application with a “Product” class and a “Cart” class. The “Product” class represents individual products, and the “Cart” class manages the shopping cart functionality.
Have a look at this python code.
class Product:
def __init__(self, name, price, quantity):
self.name = name
self.price = price
self.quantity = quantity
def update_quantity(self, new_quantity):
self.quantity = new_quantity
# Code to update quantity in other places
def calculate_total_price(self):
return self.price * self.quantity
class Cart:
def __init__(self):
self.products = []
def add_product(self, product):
self.products.append(product)
# Code to update cart-related data
def remove_product(self, product):
self.products.remove(product)
# Code to update cart-related data
def calculate_cart_total(self):
total = 0
for product in self.products:
total += product.calculate_total_price()
return total
In the above code, both the “Product” and “Cart” classes contain code related to updating data and performing calculations. If there is a change in the data structure or calculation logic, you would need to modify both classes, leading to shotgun surgery.
The Solution:
To address this code smell, we can extract the calculation logic into separate classes, such as “ProductCalculator” and “CartCalculator”, to encapsulate the responsibility of calculating prices and totals.
In this refactored code, the “ProductCalculator” class is responsible for calculating the total price of a product, while the “CartCalculator” class calculates the total price of the cart. The “Product” and “Cart” classes focus solely on managing the data and operations relevant to their respective responsibilities.
class Product:
def __init__(self, name, price, quantity):
self.name = name
self.price = price
self.quantity = quantity
class ProductCalculator:
@staticmethod
def calculate_total_price(product):
return product.price * product.quantity
class Cart:
def __init__(self):
self.products = []
def add_product(self, product):
self.products.append(product)
# Code to update cart-related data
def remove_product(self, product):
self.products.remove(product)
# Code to update cart-related data
def calculate_cart_total(self):
total = 0
for product in self.products:
total += ProductCalculator.calculate_total_price(product)
return total
class CartCalculator:
@staticmethod
def calculate_cart_total(cart):
total = 0
for product in cart.products:
total += ProductCalculator.calculate_total_price(product)
return total
Now that you have a clear understanding of the problem and know the solution, let’s determine if GitHub Copilot can identify/fix this code smells or not.
GitHub Copilot’s Result for Shotgun Surgery
Here’s the prompt I used:
# Find code smells in the code above and refactor it.
Output:
GitHub Copilot returned the same code that I mentioned in the “Shotgun Surgery Code Smell (The Challenge)” section. Meaning that it has no idea of how to fix it.
Can GitHub Copilot Write Unit Tests?
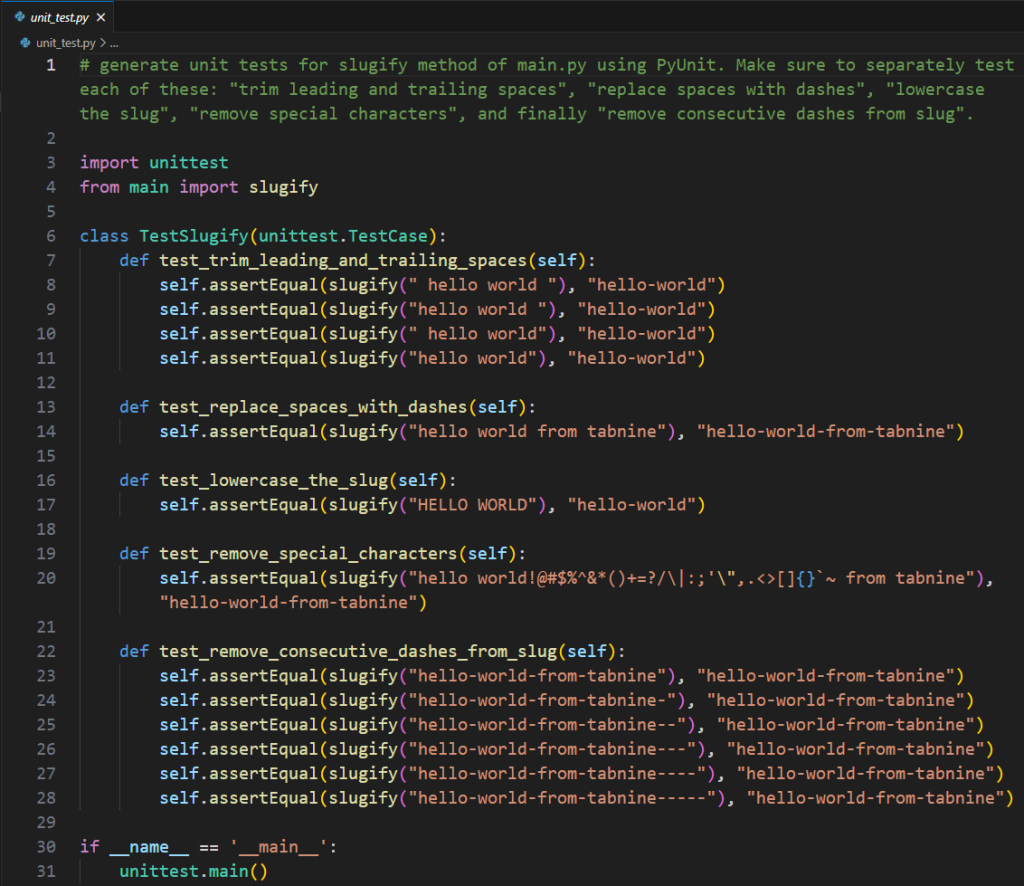
Absolutely! GitHub Copilot can definitely help with writing unit tests. It is actually one of its most valuable features.
When developing an application, it is important to write unit tests to ensure that the code functions correctly. However, writing these tests can be time-consuming and requires additional effort.
GitHub Copilot is designed to make the process of writing unit tests easier and more efficient. It can provide suggestions and generate code snippets for creating unit tests, which can save developers time and increase productivity.
For companies that prioritize test-driven development, GitHub Copilot can be a valuable tool in accelerating their testing efforts and improving overall code quality.
Here’s an example screenshot of unit test that was generated by GitHub Copilot.
Can GitHub Copilot Refactor Code?
Yes, GitHub Copilot can provide suggestions for refactoring code to make it cleaner, more efficient, or adhere to best practices. It can help you with tasks like renaming variables, extracting methods or functions, removing duplication, and reorganizing code blocks.
Suppose you have a web application that manages a list of tasks. You have a function called “getIncompleteTasks” that retrieves all the incomplete tasks from the database. Here’s the initial implementation:
def getIncompleteTasks():
tasks = fetchTasksFromDatabase()
incompleteTasks = []
for task in tasks:
if not task.completed:
incompleteTasks.append(task)
return incompleteTasks
With GitHub Copilot, you can ask for a refactoring suggestion to make the code more concise.
Here’s the prompt I used:
# refactor the above code to use list comprehension
By the way, I only added the word “refactor” in the comment. The rest of the prompt was suggested by Copilot.
Here’s the Refactored Code:
def getIncompleteTasks():
tasks = fetchTasksFromDatabase()
return [task for task in tasks if not task.completed]
Copilot suggests this refactoring based on common patterns and best practices. In this case, it replaces the explicit loop and appending to a list with a more concise list comprehension, improving the readability of the code.
Translate Code from One Language to Another
This question has no specific answer. Copilot can surely understand code in many programming languages. And hence it has the ability to translate some code from one language to another.
However, based on my personal experience with Copilot, its code translation capabilities are limited and less reliable, particularly when dealing with complex code. It tends to struggle with translations in such cases.
If you really want a bit better solution for code translation, then you can try GitHub Copilot Labs. It offers experimental features such as code translation for GitHub Copilot.
Software Documentation Using Copilot
One of the key features of Copilot is code explanation. It can understand your source code in no time and then it is ready to answer all your questions related to the code.
You can use this feature to write software documentation.
Imagine the amount of time you could save if you were relieved from the task of writing software documentation on your own.
Agent Mode – A Step Toward Autonomous Coding
Editor’s View: Surprisingly powerful, but still early-stage for complex projects.
GitHub Copilot’s new Agent Mode takes a big leap toward autonomous coding. It doesn’t just suggest lines of code anymore—it can now execute full development tasks on your behalf. For example, you can ask it to “refactor this class to use dependency injection,” and it will not only do the job but also check for issues and iterate on the fix.
What makes Agent Mode unique is that it can:
- Reason across files, not just the current one.
- Understand your intent, thanks to contextual understanding across the codebase.
- Self-correct its output based on runtime errors and logs.
In my testing, Agent Mode worked well for routine tasks like boilerplate generation, dependency upgrades, or converting function-based components to classes. However, for more abstract logic or multi-service coordination, it occasionally lost context or needed further clarification.
Verdict: This is a game-changer for solo developers and early prototyping. In team or enterprise environments, human oversight is still essential.
Vision Input – AI That Sees What You Mean
Editor’s View: Innovative and promising, but not perfect.
One of the most interesting features GitHub Copilot introduced is Vision Input—the ability to process screenshots, UI mockups, or error messages and generate actionable code or fixes based on them.
I uploaded a Figma mockup and asked Copilot to “generate the React code for this component.” The result? A decent baseline UI with correct layout and tailwind classes. Similarly, when I uploaded a screenshot of a Python stack trace, Copilot offered a potential fix and even explained what caused the error.
Use cases where Vision Input shines:
- Translating UI mockups into front-end components.
- Debugging visually—just upload an error screenshot.
- Enhancing accessibility by letting non-coders participate in ideation.
That said, Vision Input sometimes fails to interpret non-standard visuals or complex layouts. And it’s still learning how to handle interactions or animations.
Verdict: A futuristic feature that can speed up front-end work, especially when collaborating with designers or QA testers.
Code Review – AI Assistant That Points Out Flaws
Editor’s View: Excellent for basic reviews, but lacks deeper architectural insight.
The new Code Review feature in GitHub Copilot can now act like your AI-powered reviewer. When you open a pull request, Copilot analyzes the diff, highlights potential issues, and even suggests fixes. It flags things like:
- Unused imports or variables
- Missing null checks
- Inefficient loops or memory allocations
- Inconsistent naming patterns
For common pitfalls and performance problems, Copilot’s review is fast and accurate. It helped me catch a few minor bugs I would have otherwise missed. It even suggested better function names and added comments to improve readability.
However, Copilot Review currently falls short when:
- Evaluating architectural decisions
- Understanding business logic constraints
- Enforcing project-specific conventions (unless manually prompted)
Verdict: A great assistant to catch low-hanging issues and clean up code fast—but don’t skip your senior dev’s review just yet.
Is GitHub Copilot Worth It?
GitHub copilot is worth it if you use it as an assistant. Do not expect it to magically write complete source code for you. Do not expect it to automate your software development. It requires manual work also.
Copilot is particularly good at helping you with software documentation, writing unit test, and refactoring code.
No doubt, Copilot provides good code completions. But sometime the suggestions you get are completely irrelevant. So, you cannot rely on it all the time. You may need to provide a bit more context so Copilot can understand the requirements better.
Finally, in just $10 a month, an individual developer could produce way more code than he/she usually write. So, GitHub Copilot is worth it.
For now, GitHub Copilot is not worth it if you want to detect code smells or translate code from one programming language to another. For that you must look for some alternatives. An excellent option is to try Bito (an AI Coding Assistant) that offers way more features than Copilot such as AI that understands your local code out of the box, AI Code Completions, detect/fix code smells, etc.
Is GitHub Copilot Safe to Use at Work?
To deliver quality suggestions, GitHub Copilot frequently sends code snippets from your project to GitHub’s server. These code snippets are mostly used for context and are deleted automatically when the Copilot’s response is generated.
If your organization does not allow you to send code outside their premises, you must look for an alternative offering self-hosting and offline access.
Regarding privacy, it is important to note that GitHub may train its AI model on snippets of code from your repositories to improve Copilot’s suggestions. However, if you prefer not to share your code for this purpose, you have the option to disable it.
Just go to your GitHub account’s settings page and click “Copilot” from the sidebar. Now, uncheck the box “Allow GitHub to use my code snippets for product improvements” and press the “Save” button.
How GitHub Copilot Compared With its Alternatives
GitHub Copilot lacks many key features that are available in some of its alternatives. For example, these days many AI Coding Assistant tools are packed with an AI Chat feature. It enables users to have a conversation with AI, just like ChatGPT.
This feature is something that drastically improves the user experience.
Similarly, Copilot does not understand your entire code base. It only takes context from currently opened tabs in your coding editor/IDE. As of writing this GitHub Copilot review, there is only one alternative known as Bito that understands your local code out of the box.
Bito is one of the highest-rated Copilot alternative extensions on the Visual Studio Code marketplace. It also has a free plan, so why don’t you try it yourself?
Some other GitHub Copilot alternatives include:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI)
- Amazon CodeWhisperer
- Tabnine
- Replit Ghostwriter
- Cursor AI
- Windsurf (formerly CodiumAI)
Each of these GitHub Copilot alternatives offer different strengths in terms of integration, supported languages, and AI model capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is GitHub Copilot Worth the Money for Freelance Developers?
GitHub Copilot can be beneficial for freelance developers. It can help speed up the coding process by generating code suggestions based on the context. This can save time and increase productivity, allowing freelancers to complete projects more efficiently.
If the freelancer in question has good coding proficiency and their work involves repetitive tasks, then Copilot will be worth the money. For just $10, they could complete a significantly higher number of orders compared to not using Copilot.
Is GitHub Copilot Worth it for Software Companies?
GitHub Copilot can be a valuable tool for small tech companies. But I do not think it could add value for teams working on large-scale projects with complex codebases. No doubt it provides good code suggestions, but it only has limited context from a few opened tabs. Therefore, it will not be very useful for large-scale projects.
There are some better alternatives that can understand entire codebases. Bito is a market leader in this field because it indexes your code locally and hence offers more precise suggestions.
Is GitHub Copilot Free for Students?
Yes, GitHub Copilot is available for free to verified students. To be eligible, you need to meet the following requirements:
- You must be currently enrolled in an educational institution.
- You should have a verifiable school-issued email address or be able to provide documents that demonstrate your current student status.
Is GitHub Copilot Worth it for Students?
GitHub Copilot offers free access to students. It can provide helpful code suggestions and serve as a learning aid, assisting students in understanding programming concepts and syntax. It may help them save time and overcome coding challenges more easily.
Additionally, GitHub Copilot can expose students to different coding styles and best practices, enhancing their learning experience. However, students should also be cautious and ensure they understand the code generated by the tool to avoid blindly relying on it.
Does GitHub Copilot Steal Your Code?
GitHub Copilot does not intentionally steal codes. But it can use your code to train its AI model. If you want to prevent that, simply go to your GitHub account’s settings page, and click “Copilot” from the sidebar. Now, uncheck the box “Allow GitHub to use my code snippets for product improvements” and press the “Save” button.
Can I Use GitHub Copilot at Work?
Yes, you can use GitHub Copilot at work. It helps small teams to be more productive while writing source code for apps. It can be used in various development environments, including professional settings. However, it is important to ensure that your organization’s policies and guidelines allow the use of AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot.
Is GitHub Copilot Safe to Use at Work?
GitHub Copilot is generally considered safe to use at work. It is developed by reputable organizations and is designed to provide code suggestions to assist developers. However, as with any software, there may be potential security concerns or risks associated with using GitHub Copilot. It is recommended to review the security and privacy measures provided by GitHub and OpenAI, and to consult with your organization’s IT or security department to ensure compliance with any specific requirements or policies.
Is GitHub Copilot Open Source?
GitHub Copilot is not open source. While GitHub is built on open-source technologies and supports numerous open-source projects, GitHub Copilot itself is a proprietary tool developed by GitHub in collaboration with OpenAI. The underlying AI model and code generation capabilities are not openly accessible or modifiable by the user.
Does GitHub Copilot Work Offline?
No, GitHub Copilot does not work offline. It relies on a connection to the internet to function properly. The AI model and code generation processes are performed on remote servers, which require an active internet connection for GitHub Copilot to provide code suggestions in real time.
How to Enable GitHub Copilot in VSCode?
To enable GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code (VSCode), follow these steps:
- Install the GitHub Copilot extension from the Visual Studio Code marketplace.
- After installation, sign in to your GitHub account within the VSCode editor if prompted.
- Make sure you have an active subscription to GitHub Copilot. It costs $10 per month for individuals.
- GitHub Copilot should now be enabled, and you can start using it by opening a code file and typing in your desired programming language.
Is GitHub Copilot Better Than ChatGPT?
GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT serve different purposes and have different functionalities. GitHub Copilot is specifically designed to assist developers by providing code suggestions, while ChatGPT is an AI language model developed for generating human-like text responses in conversational contexts.
GitHub Copilot can be a valuable tool for developers, especially when working on coding tasks, as it can help speed up the coding process and provide suggestions based on the context. It focuses on generating code snippets and completing code patterns.
On the other hand, ChatGPT is designed to understand and generate text based on the input it receives. It is more suitable for answering a wide range of questions, engaging in conversations, or generating creative written content.
Ultimately, the choice between GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT depends on the specific needs and use case. If you are primarily looking for code generation assistance, GitHub Copilot would be more suitable. If you need a conversational AI model for general text generation, ChatGPT would be a better option.
How accurate is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot generates useful suggestions around 55–70% of the time depending on the programming language and task complexity. Accuracy improves with clear, well-structured code and frequent usage.
What are some key benefits of GitHub Copilot?
- Reduces time spent on boilerplate code.
- Increases developer productivity.
- Helps onboard junior developers faster.
- Improves code consistency across teams.
- Integrates seamlessly into popular IDEs.
What are the limitations of GitHub Copilot?
- May generate outdated or insecure code.
- Lacks deep understanding of proprietary or complex systems.
- Requires internet access for real-time suggestions.
- No native test coverage or static analysis integration.
- Limited fine-tuning or customization for individual users.
How to use GitHub Copilot effectively?
- Write clear function names and comments to guide suggestions.
- Review all generated code for correctness and security.
- Use Copilot for repetitive patterns, boilerplate, and documentation.
- Pair Copilot with linters and test suites.
- Update Copilot settings to match your workflow and language preferences.
What is GitHub Copilot ROI?
Developers using Copilot report up to 55% productivity gain. Teams can ship features faster, reduce bugs early, and save time on documentation. ROI improves significantly in teams adopting it for both junior and senior developers.
GitHub Copilot free vs paid
| Feature | Free Plan | Paid Plans (Pro, Pro+, Business) |
|---|---|---|
| Code Completions | 2,000/month | Unlimited |
| Chat/Agent Requests | 50/month | Unlimited or scaled with tier |
| Model Access | GPT-4.1, Claude 3.5 | GPT-4.5, Claude 4, Gemini 2.5, o3 |
| Coding Agent Access | No | Yes (Pro+ and Enterprise) |
| Use Case Suitability | Hobby projects, light coding | Professional development, production apps |
Conclusion
In this comprehensive GitHub Copilot review, I have tried my best to answer your question “Is GitHub Copilot Worth It?” in detail.
First, I have shared my personal experience with each feature of GitHub Copilot, discussing whether they are worth using or not. This will provide you with a better understanding of the strengths of GitHub Copilot and areas where it needs improvement.
The value of GitHub Copilot varies depending on individual needs and circumstances. It can enhance productivity for freelance developers, improve code quality for software companies, and facilitate learning for students.
With careful use, Copilot can be a valuable coding aid, but understanding its limitations is crucial. Users must validate suggestions and ensure alignment with standards and requirements. The tool’s ultimate value depends on coding proficiency, project complexity, and budget considerations.