On-demand AI code reviews
Save 1 day per sprint
Let AI take the first pass
Uplevel junior engineers
Enterprise- grade security
We don't store or train AI on your code
No credit card required
Trusted by thousands of developers worldwide
See Bito at work
Built for today’s development teams
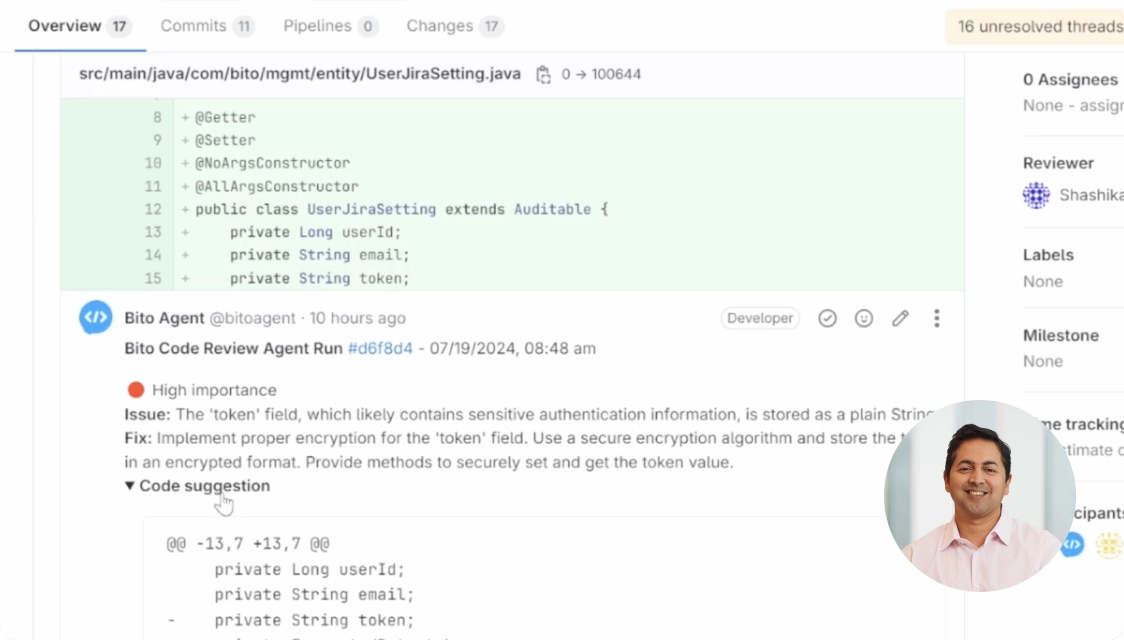
Get on demand feedback
Bito stands apart by providing the best AI feedback — in your IDE or in your Git provider.
Ship faster, save time
Bito can help your team win back 1 day per sprint cycle without adding headcount.
Uplevel junior engineers
Bito turns junior engineers into high performers by delivering precise suggestions and best practices with educational context.
Reduce regressions
Bito focuses on security, scalability, performance, and code understanding before code gets to peer review, reducing conflicts in code review.
AI that understands your code
Bito deeply understands your codebase to do a human-like code review.
See how we do it